Quantum computing is rapidly evolving, promising exponential speed-ups for tasks ranging from cryptography and drug discovery to complex simulations. However, one significant challenge remains: quantum errors. To unlock the full potential of quantum technology, we must address these errors efficiently and accurately.
In this blog, we’ll explore the role of quantum error correction, the necessity of leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) for error detection and correction, and how these technologies collaboratively enhance the performance of quantum algorithms.
1. What is Quantum Error Correction (QEC)?
Quantum Error Correction (QEC) is a set of techniques designed to protect quantum information from errors that inevitably arise due to quantum decoherence and operational imperfections. Quantum decoherence occurs when quantum bits (qubits) lose their delicate quantum states due to environmental interactions, causing quantum noise and errors. Unlike classical error correction, quantum error correction must address errors without directly observing the quantum states themselves, as direct observation collapses these fragile states. QEC uses redundancy, encoding a single logical qubit into multiple physical qubits. This redundancy enables indirect measurement of “error syndromes,” revealing the presence and type of errors without disturbing the protected quantum information, allowing the system to correct these errors and maintain the integrity of quantum computations.
QEC is essential for quantum computing because quantum states are incredibly sensitive to even slight disturbances. Without effective error correction, quantum algorithms rapidly accumulate errors, leading to inaccurate results and potentially rendering quantum computations impractical.
2. Why Do We Need AI for Quantum Error Detection Instead of Relying on Humans?
-
Agentic AI and Tailored Noise Modeling: An agentic AI can reconstruct the noise models inherent in quantum computers by directly interacting with and learning from observed measurement outcomes. It can dynamically tailor error correction strategies specifically optimized for particular hardware, thereby becoming device-agnostic. Furthermore, reinforcement learning techniques enable the AI to continuously improve and adapt its strategies based on real-time feedback.
-
Scalable Foundation Models: By developing a foundation model, AI can efficiently implement any quantum error correction code tailored to specific hardware. Such models can initially be trained on small-scale systems and subsequently applied to larger, more complex systems. This scalability greatly surpasses traditional human-designed approaches, as the AI inherently understands the nuances and operational behaviors of the quantum hardware better.
3. How Does AI-Powered Quantum Error Correction Work Alongside Quantum Algorithms?
To illustrate the integration of AI into quantum error correction, consider the following workflow:
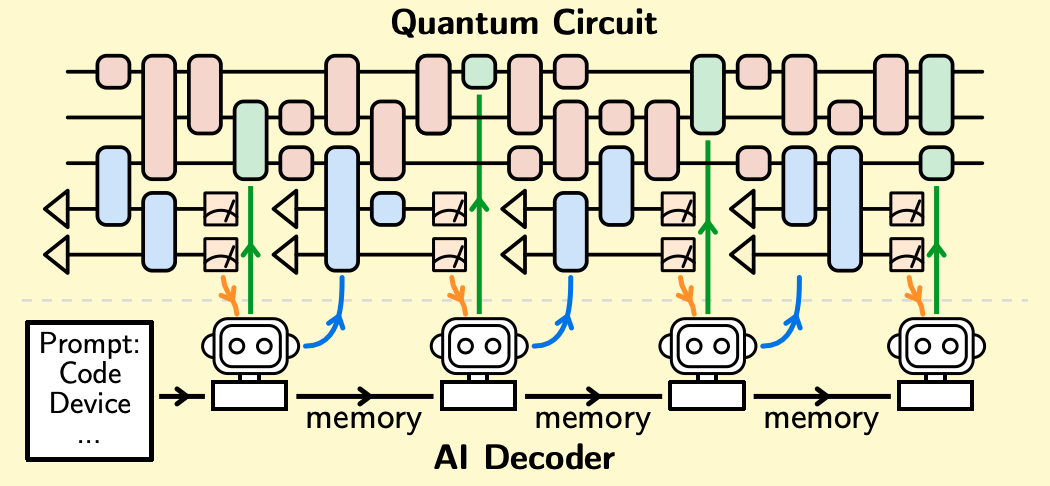
A schematic diagram will show how the AI interacts directly with the quantum computer. The AI begins by taking a quantum error correction code, such as the LDPC code, represented as a “Tanner graph,” as input. It then proposes which syndrome qubits should be measured. Measurement outcomes from these qubits are fed back into the AI, which predicts appropriate quantum gate operations (actions) to correct detected errors. This process ensures real-time error detection and correction.
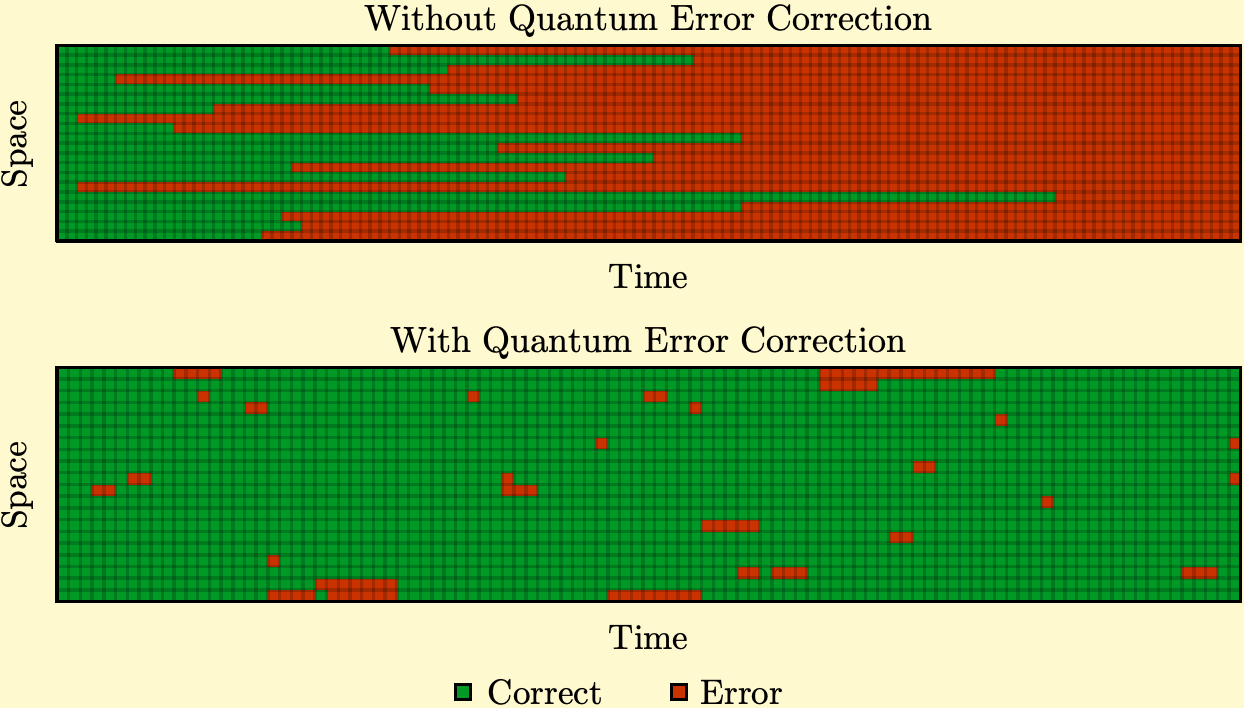
Additionally, the comparative figure above highlights the benefit of AI-assisted quantum error correction. In the upper panel, quantum errors accumulate unchecked as the quantum algorithm proceeds, eventually overwhelming and crashing the algorithm. In contrast, the lower panel illustrates how quantum error correction continuously mitigates errors during computation, preventing error accumulation and allowing the quantum algorithm to run smoothly and reliably.
Conclusion
Combining AI with quantum computing not only accelerates the development of robust quantum technologies but also ensures quantum algorithms can deliver on their transformative promises. Our commitment is to lead the way in this exciting interdisciplinary frontier, harnessing artificial intelligence to make quantum computing practical, powerful, and reliable.
Stay tuned for more updates as we embark on this exciting journey into the quantum future!